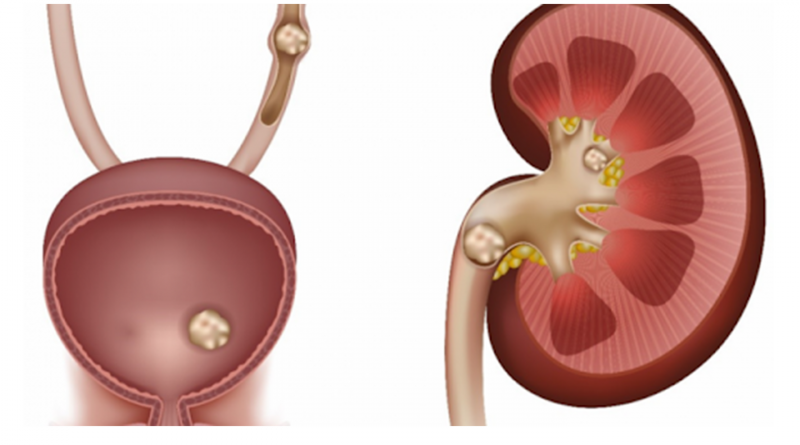
Urinay Stone Diseases
It is a common health problem in our country as it is in the neighbourhood regions. Stone formation / occlusion can be observed anywhere in kidneys, ureters (thin urinary tract between kidney and bladder), bladder and urethra (external urinary canal). They can be detected at any age, including children under 1 year. Altough symptoms are abdominal pain, side pain, darkening of the urine color, blood in urine, and burning during urination; some patients may not show any symptoms for a long time. It is observed more frequently in poor nutritional quality and poor socioeconomic developed regions. In children with a history of stone in family members, monitoring of stones indicates that genetic predisposition is effective. Urinary system stone disease is a disease with high probability of recurrence. Therefore, in order to prevent the formation of new stones, to prevent the growth of existing stones, fluid intake and nutritional habits should be severely adjusted, and even if the physician deems appropriate, long-term use of certain drugs is required.
Urinary system stones differ in their structures. Although 80% of the cases contain calcium stones , they are also composed of stones of different structures (cystine stones, uric acid stones, infection stones). Knowing the type of stone that causes the disease is important in determining our treatment approaches.
In the diagnosis of the disease, urine examination, urine culture, biochemical analysis of collected urine for 24 hours, some specific blood tests, and physical analysis of the stone (itself or part of it) are performed. In the determination of the location and size of the stone, imaging tests such as X-ray, urinary system ultrasonography and computed tomography can be planned on a patient basis. In this way, the presence, number, location, component of the stone and the problem caused by it are drawn.
Although some of these stones pass through spontaneously with or without medication, some of them may require intervention. With the help of developing technology, we can intervene urinary system stones in pediatric patients with many methods. Thanks to these new methods, open surgery (skin cut operations) has almost no place in the treatment of stone diseases.
Stone Breaking with Extra-Body Shock Wave (SWL): It is mostly used in the treatment of kidney and ureteral stones. It is performed under sedation (mild anesthesia). Sound waves sent from outside the body fractures the stone into pieces by focusing on it. After the procedure, these stone particles are expected to be excreted by the urine stream. More than one session may be required for complete stone-free result. The success of the treatment depends on the hardness of the stone structure, and therefore its strength against the sound wave.
Endoscopic procedures (URS, RIRS, Cystolithotripsy): It can be applied to stones all over the urinary system. General anesthesia and operating room conditions are required. It can be made by entering through the urinary canal without creating an incision or entry hole in the body. By using thin cameras and laser breakers, the stone can be fractured and excreted on its own free fall, or also in some cases removing some of the stone during surgery is required. Although the stone-free rate is high, the chance of success may be low in patients with very narrow urinary tract or very young age due to technical inability.
Percutaneous (through the skin) interventions: Usually applied to kidney and bladder stones. It is performed under general anesthesia and operating room conditions. The stone is drilled with special tools and broken, afterwards the stone is taken out (PCNL). Stone-free rates are high. The size of the drilled hole has been reduced to millimeters (MiniPerc, microPerc) in parallel to the developing technology.
Surgical success rates in the pediatric age group have increased depending on the development in technology. However, it should be noted that the technique to be used should be given according to the urologist’s experience, the condition of the patient and the characteristics of the stone.
Another important point in the treatment as well as surgery is planing how to prevent from re-formation. For this purpose, it is important to adopt appropriate fluid intake and to ensure regular drug use in necessary cases. It should be remembered that without this planings treatment remains insufficient.
